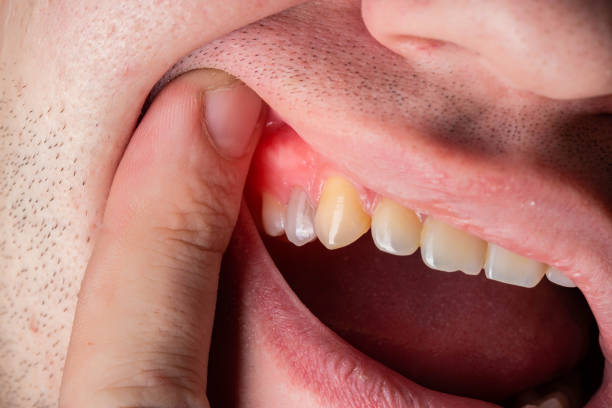
Gum swelling, or gingival inflammation, is a common oral health issue that can result from various factors, including poor oral hygiene, bacterial infections, or even ill-fitting dental appliances. Addressing gum swelling promptly is crucial to preventing more severe conditions like periodontitis. This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to treat gum swelling using effective, professional remedies and prevention techniques.
What Causes Gum Swelling and Inflammation?
Understanding the root cause of gum swelling is essential in determining the right treatment. Some of the most common causes include:
- Gingivitis: A mild form of gum disease caused by plaque buildup.
- Periodontitis: Advanced gum disease that leads to gum recession and bone loss.
- Plaque and Tartar Buildup: Bacteria accumulation on teeth and gums.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inconsistent brushing and flossing habits.
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, menopause, and puberty can contribute to swollen gums.
- Ill-Fitting Dental Appliances: Braces, dentures, or retainers that do not fit properly can irritate the gums.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of essential vitamins and minerals like Vitamin C can weaken gum health.
- Medications: Some prescriptions, including certain blood pressure medications, may cause gum inflammation.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Diabetes and autoimmune diseases can contribute to gum problems.
How Can You Treat Gum Swelling Professionally?
Treating gum swelling requires a combination of professional dental treatments, medication, and an improved oral hygiene routine. Below are the best approaches:
Professional Dental Cleaning (Scaling & Root Planing)
- Scaling removes plaque and tartar from the teeth and below the gumline.
- Root planing smooths the tooth roots to prevent bacteria accumulation.
- Recommended for patients with gingivitis or early-stage periodontitis.
Prescription Mouthwashes
- Contain antiseptic agents such as chlorhexidine to kill bacteria.
- Reduce inflammation and prevent further plaque formation.
- Should be used under the guidance of a dentist.
Antibiotics for Gum Infection
- Prescribed in cases where bacterial infections contribute to swelling.
- Doxycycline, amoxicillin, or metronidazole may be used.
- Can be administered in gel form, tablets, or mouth rinses.
Anti-Inflammatory Medications
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen reduce swelling and discomfort.
- Should be taken as directed to avoid overuse.
Correcting Dental Appliances
- Braces, retainers, or dentures that do not fit properly should be adjusted by a dentist.
- Poorly fitted appliances can cause continuous irritation and gum swelling.
Advanced Periodontal Treatments
| Treatment | Description |
| Laser Therapy | Minimally invasive removal of infected tissue. |
| Gum Flap Surgery | Lifting the gums to remove bacteria and tartar. |
| Bone Grafting | Rebuilding bone lost due to periodontitis. |
| Guided Tissue Regeneration | Stimulating gum and bone regrowth. |
What Are the Best Preventive Measures for Gum Swelling?
Preventing gum swelling is more effective than treating it. Here are key strategies to maintain gum health:
Maintain a Strong Oral Hygiene Routine
- Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristle toothbrush.
- Floss once a day to remove plaque between teeth.
- Use an antibacterial mouthwash to kill bacteria.
- Replace your toothbrush every 3 months or when bristles fray.
Nutritional Support for Gum Health
| Nutrient | Role in Gum Health | Food Sources |
| Vitamin C | Aids in gum healing and reduces inflammation. | Citrus fruits, bell peppers, leafy greens. |
| Calcium | Strengthens teeth and gums. | Dairy products, almonds, leafy greens. |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Reduces inflammation. | Salmon, walnuts, flaxseeds. |
| Probiotics | Supports healthy oral bacteria. | Yogurt, kefir, fermented foods. |
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Gum Irritation
- Avoid smoking, as it increases the risk of gum disease.
- Limit alcohol consumption, which can dry out the mouth.
- Stay hydrated to maintain saliva production and flush bacteria.
- Reduce sugar intake, as it fuels bacterial growth in the mouth.
When Should You See a Dentist for Gum Swelling?
Seek professional dental care if you experience:
- Persistent gum swelling lasting more than two weeks.
- Bleeding gums without apparent cause.
- Pus formation between the teeth and gums.
- Severe pain affecting eating and speaking.
- Bad breath that does not improve with oral hygiene.
Why Choose M&M Dental for Professional Gum Care?
If you are struggling with persistent gum swelling, it is crucial to seek expert care. M&M Dental is dedicated to providing advanced periodontal care using the latest techniques and technology. Our team of experienced dental professionals ensures thorough diagnosis and treatment tailored to your specific needs. Whether you require deep cleaning, antibiotic therapy, or laser gum treatment, we prioritise your oral health and comfort. Don’t ignore gum inflammation—schedule a consultation with M&M Dental today to prevent long-term dental complications.
References
- Australian Dental Association. (2024). Gum Disease Prevention & Treatment.
- Better Health Channel (Victoria). (2024). Gingivitis & Periodontal Disease.
- Oral Health Foundation Australia. (2024). Maintaining Healthy Gums.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Can swollen gums go away on their own?
Mild gum swelling caused by temporary irritation may subside with proper oral hygiene. However, if swelling persists beyond two weeks, professional evaluation is recommended.
- What is the fastest way to reduce gum swelling?
The most effective way to reduce swelling is to maintain proper oral hygiene, use a prescribed antibacterial mouthwash, and take NSAIDs if advised by a dentist.
- Can gum swelling indicate a serious dental condition?
Yes, persistent gum inflammation can be a sign of underlying issues like gingivitis or periodontitis, which require professional treatment.
- How can I prevent my gums from swelling in the future?
Practise good oral hygiene, attend regular dental check-ups, avoid smoking, and ensure a well-balanced diet rich in essential nutrients.
- Is gum swelling always due to gum disease?
Not necessarily. It can also be caused by hormonal changes, medications, or ill-fitting dental appliances. Identifying the cause helps determine the right treatment.
- Should I stop flossing if my gums are swollen?
No. Gentle flossing is essential to remove plaque and bacteria. Avoid aggressive flossing, which can irritate the gums further.