The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is an essential part of your body, facilitating the movement of your jaw. However, when this joint is not functioning properly, it can lead to a variety of symptoms affecting both the jaw and the surrounding areas, including the gums. One of the less well-known consequences of TMJ disorder is gum swelling. This blog will explore how TMJ can contribute to gum swelling, the symptoms to look out for, and the methods of relief.
What Is TMJ and How Does It Affect the Jaw?
TMJ stands for temporomandibular joint, which connects the jawbone to the skull. This joint is essential for various functions, such as speaking, chewing, and yawning. However, when this joint is compromised by dysfunction, it can lead to a condition called temporomandibular joint disorder (TMD). TMD can cause discomfort and pain, often radiating to the surrounding muscles and tissues, including the gums.
TMJ disorder is often characterised by symptoms such as:
- Jaw pain or soreness
- Clicking or popping noises when moving the jaw
- Limited jaw movement
- Headaches and facial pain
- Tenderness in the gums
Can TMJ Cause Gum Swelling?
While TMJ disorder is primarily related to jaw pain and dysfunction, it can indirectly cause gum swelling. The reason for this is the pressure exerted by the jaw muscles when they are tense, misaligned, or overworked due to jaw clenching or teeth grinding (bruxism), which are both common in people with TMJ issues.
How Does TMJ Contribute to Gum Swelling?
- Muscle Tension: The muscles around your jaw can become tense and inflamed due to TMJ. This muscle tension can create pressure on the gums, leading to swelling and discomfort.
- Bruxism (Teeth Grinding): One of the symptoms of TMJ is bruxism, which is the involuntary grinding or clenching of teeth. This action can strain the gums and cause inflammation, resulting in swelling.
- Jaw Misalignment: TMJ often results in the misalignment of the jaw. When the jaw is misaligned, it can lead to improper contact between the teeth, which in turn can cause pressure on the gums.
What Are the Symptoms of Gum Swelling Caused by TMJ?
When gum swelling is related to TMJ disorder, it may not always present as the classic signs of gum disease, but the symptoms can still be quite noticeable. Here’s what to look for:
- Pain in Jaw or Face: You may experience pain that radiates to your gums due to muscle strain and tension in the jaw.
- Tender Gums: Swelling around the gums can occur because of the pressure exerted by clenching or grinding teeth.
- Headaches: TMJ-related tension often leads to headaches, which may intensify the pain around the gums.
- Clicking or Popping Sounds: If you hear clicking or popping sounds when moving your jaw, it may indicate jaw misalignment contributing to gum swelling.
- Limited Jaw Movement: Difficulty opening or closing your mouth due to jaw dysfunction can increase the risk of gum discomfort.
How Can You Relieve Gum Swelling Caused by TMJ?
The relief of gum swelling caused by TMJ is possible, especially with the right treatment approach. Here’s a look at some of the methods that can help:
Dental Splints or Mouthguards
Mouthguards are often prescribed for individuals who grind their teeth or clench their jaw. By wearing a custom-made splint or mouthguard, pressure on the gums is reduced, and further swelling is prevented. Mouthguards can be worn at night or during times of increased stress to protect both your teeth and gums.
Jaw Exercises
Incorporating specific jaw exercises into your daily routine can help to relieve muscle tension. These exercises aim to strengthen the jaw muscles and improve mobility, reducing the strain that leads to gum swelling.
Anti-inflammatory Medications
Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications, such as ibuprofen, can help to reduce both the swelling and discomfort in the gums. If needed, your dentist may prescribe stronger medications to manage pain and inflammation more effectively.
Heat or Cold Therapy
Applying a heat pack or cold compress to the jaw can reduce inflammation and muscle tension. A cold pack is particularly useful for reducing immediate swelling, while a heat pack can help relax tight muscles.
Stress Management Techniques
Since stress is a common trigger for bruxism, which contributes to TMJ and subsequent gum swelling, managing stress is an essential part of treatment. Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help reduce stress and prevent the muscle strain associated with TMJ.
Physical Therapy
In some cases, physical therapy may be recommended to help alleviate TMJ symptoms. A therapist can guide you through exercises that improve jaw function and reduce pressure on the gums.
Can TMJ Affect Other Areas of Your Health?
While the primary symptoms of TMJ disorder are related to the jaw and surrounding muscles, the condition can also have a broader impact on overall health. Individuals with TMJ may experience:
- Headaches and Migraines: TMJ can lead to chronic tension in the head and neck area, triggering headaches.
- Ear Pain or Ringing: TMJ dysfunction can affect the muscles near the ears, leading to discomfort or even tinnitus (ringing in the ears).
- Neck and Shoulder Pain: The stress and strain on the jaw can extend to the neck and shoulders, causing pain and discomfort.
These symptoms often exacerbate the discomfort associated with TMJ, further complicating the treatment of gum swelling and other related issues.
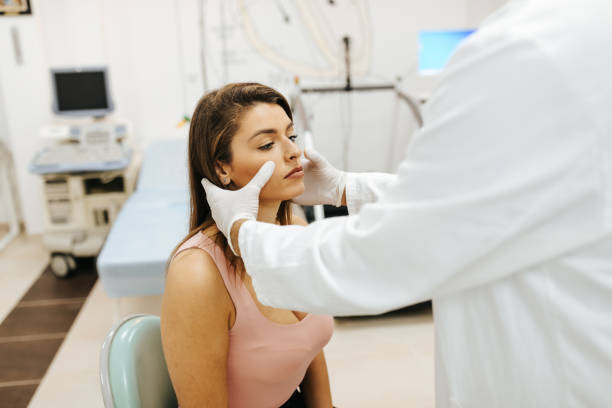
How Is TMJ Diagnosed and Treated by a Professional?
If you suspect that TMJ is causing your gum swelling, it’s important to consult with a dentist or healthcare professional who can diagnose the condition. The diagnostic process typically includes:
- Medical History Review: A thorough review of your medical history, including any signs of teeth grinding or jaw discomfort.
- Physical Examination: A dentist will examine the jaw and check for signs of misalignment, tenderness, or swelling in the gums.
- Imaging Tests: In some cases, X-rays or MRIs may be used to assess the joint and surrounding tissues for any damage or misalignment.
Once diagnosed, treatment options will vary based on the severity of the condition and may include the use of mouthguards, medications, or even surgery in extreme cases.
M&M Dental Care: Your Solution to TMJ and Gum Health
At M&M Dental Care, we understand the connection between TMJ disorders and the discomfort it can cause to your gums and overall oral health. Our team of skilled dental professionals offers comprehensive evaluations and tailored treatment plans to help alleviate symptoms of TMJ, reduce gum swelling, and restore your jaw’s functionality. With advanced diagnostic tools and personalised care, we’re here to ensure that your oral health is in optimal condition. Don’t let TMJ symptoms disrupt your life — book an appointment with us today!
References
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Can TMJ cause gum pain and swelling? Yes, TMJ disorder can lead to gum pain and swelling, primarily due to muscle tension, teeth grinding, or jaw misalignment associated with the condition.
- What are the primary causes of TMJ? TMJ is often caused by jaw injury, teeth grinding (bruxism), jaw misalignment, or stress, which leads to inflammation and discomfort.
- How can I treat TMJ-related gum swelling? Treatments may include dental splints, anti-inflammatory medications, jaw exercises, heat or cold therapy, and stress management techniques.
- Is TMJ a permanent condition? TMJ can be managed and symptoms can be alleviated with treatment. However, some individuals may experience recurring symptoms, especially if bruxism or jaw misalignment continues.
- What is bruxism, and how does it affect TMJ? Bruxism is the grinding or clenching of teeth, often occurring during sleep. This can exacerbate TMJ symptoms by adding strain to the jaw muscles, contributing to gum swelling.
- When should I see a dentist for TMJ issues? If you experience persistent jaw pain, gum swelling, or difficulty moving your jaw, it’s important to consult a Dentist Near Me for an evaluation and appropriate treatment.